< Return to trials
Gout
Overview
Lillestol Research has performed multiple trials involving the gout indication/diagnosis. The trials have varied in phase from the investigational product phase to observational, as well as varied in enrollment criteria and trial duration. Gout is one of our most experienced trial indications to recruit to. The multitude of trials that we have performed in this indication has developed a robust research patient database of over 700 individuals with a gout diagnosis that would be interested in clinical trial participation.
Spotlight Trial(s)
- This was an investigational product vs. marketed product and placebo in patients with gout and various degree of renal function and/or impairment. Lillestol Research was able to successfully meet and far exceed the sponsor’s enrollment expectation randomizing 28 patients to the trial. Recruitment is ongoing.
- This was an investigational and marketed product combination vs. a marketed product alone in patients with tophaceous gout. This trial evaluated the effect of these products in lowering serum uric acid and resolving tophi. Lillestol Research was able to successfully meet and far exceed the sponsor’s enrollment expectation randomizing 14 patients in a 14-month enrollment period.
- This was an open-label study of after-market allopurinol in gout patients with hyperuricemia. The study will evaluate allopurinol as a urate lowering therapy (ULT). Lillestol Research was able to successfully meet and far exceed the sponsor’s enrollment expectation randomizing 31 patients in an 8-month enrollment period.
- This was a long-term cardiovascular outcomes trial comparing an investigational product vs. a marketed product in patients with gout and cardiovascular risk factors. Lillestol Research was able to successfully meet and far exceed the sponsor’s enrollment expectation randomizing 39 patients to the trial. Recruitment is ongoing.
- This was a double blind, placebo controlled study. Lillestol Research was able to successfully meet and exceed the sponsor's enrollment expectation randomizing 33 patients in a 14 month enrollment period.
Definition
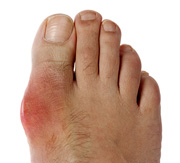
Gout is a form of arthritis. It is the body's reaction to irritating crystal deposits in the joints due to an excess of uric acid in the blood.
Description
The pain from Gout can be intense, but treatment usually works very well. Mild cases may be controlled by diet alone. Recurring attacks of gout may require long-term medication to prevent damage to bone and cartilage and deterioration of the kidneys.
Chronic gout sufferers may feel tiny, hard lumps accumulating over time in the soft flesh of areas such as the hands, elbows, feet, or earlobes. These deposits, called tophi, are concentrations of uric acid crystals and can cause pain and stiffness over time. If similar deposits form in the kidneys, they can lead to painful and potentially dangerous kidney stones.
More than 2 million Americans suffer from gout. Gout occurs more often in men than in women. Men usually develop it between the ages of 30 and 50.
Causes and Symptoms
An excess of uric acid in the blood brings on gout. Uric acid comes from two places -- produced by the body and from the diet. Any extra uric acid usually filters through the kidneys and gets passed in urine. If the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete it in the urine, crystals of sodium urate form in the joints and tendons. These crystals cause intense inflammation leading to pain swelling and redness.
The most common factor that increases your chance of gout and gout attacks is excess consumption of alcohol, mainly beer. It used to be known as "the disease of kings" since it was mainly seen in wealthy men who drank and ate too much. Now we know it can occur in anyone and can be associated with injury or surgical procedures, hospitalizations, periods of stress, or reactions to fatty meals and certain drugs such as antibiotics. Susceptibility to gout is often inherited and is often associated with other common illnesses such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Repeat attacks of gout are common if the body's uric acid level is not kept under control.
Symptoms of gout usually strike unexpectedly. Symptoms of a gout attack may include:
- Sudden, intense pain in a joint, typically the big toe or ankle, sometimes the knee, hand, or wrist
- Swelling, inflammation, and a feeling that the joint is very hot
- Extreme tenderness of the joint to even the lightest touch
- Red or purple skin around the joint
- In extreme cases, alternating chills and fever
Source
http://arthritis.webmd.com/understanding-gout-basic-information
If you have been diagnosed with gout or suffer from symptoms similar to gout, contact us today to learn more about our current study opportunities for this diagnosis.
Call us at (701) 232-7705 or toll-free at (866) 532-7705
Signup online or email our recruiter at recruiter(at)lillestolresearch(dot)com.
Your information is always kept confidential.